Summary
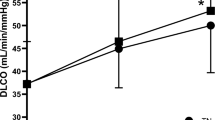
We measured pulmonary function in 12 healthy volunteers before and at 5-min intervals for 30 min following treadmill exercise of 30 min duration performed under control (20° C) and cold (−11 ° C) ambient temperatures. Post-run changes in forced vital capacity (FVC), residual volume (RV) and peak expiratory flow rate were similar between the two temperature conditions. FVC decreased slightly but significantly 5 min post-run (−0.25 ±0.201 and −0.21−0.201, for control and cold conditions respectively) and returned to baseline by 30 min. RV increased significantly post-exercise (+ 0.07 ± 0.091 and + 0.14 ± 0.11, control and cold respectively) and remained elevated for 30 min. Forced expired volume in 1 s was not significantly different following either run. Post-exercise, maximum mid-expiratory flow rate and flows at 50% and 25% of vital capacity were not significantly different between warm and cold conditions. These data suggest that changes in lung volumes following exercise under cold ambient conditions are similar to changes seen following warm exercise of similar duration. In non-asthmatics, moderate exertion under cold ambient conditions does not appear to cause clinically significant decreases in expiratory flow rates as compared to similar exertion under warm conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Thoracic Society Statement (1979) Snowbird workshop on standardization of spirometry. Am Rev Respir Dis 119:831–8
Buono MJ, Constable SH, Morton AR, Rotkis TC, Stanforth PR, Wilmore JH (1981) The effect of an acute bout of exercise on selected pulmonary function measurements. Med Sci Sports Exerc 13:290–3
Chen WY (1979) Reactivity of normal airways to short-term exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 38:277–80
Deal EC, McFadden ER, Ingram RH, Strauss RH, Jaeger JJ (1979) Role of respiratory heat exchange in production of exercise-induced asthma. J Appl Physiol 46:467–75
Fish JE, Ankin MG, Keely JF, Peterman VI (1981) Regulation of bronchomotor tone by lung inflation in asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects. J Appl Physiol 50:1079–86
Gold PM (1982) Single breath nitrogen test: closing volume and distribution of ventilation. In: Clausen JL (ed) Pulmonary function testing guidelines and controversies; equipment, methods, and normal values. Academic Press, New York, pp 105–114
Jaeger JJ, Deal EC, Roberts DE, Ingram RH, McFadden ER (1980) Cold air inhalation and esophageal temperature in exercising humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc 12:365–9
Lefcoe NM, Carter RP, Abroad D (1971) Postexercise bronchoconstriction in normal subjects and asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis 104:562–7
Mahler DA, Loke J (1981a) Pulmonary dysfunction in ultramarathon runners. Yale J Biol Med 54:243–8
Mahler DA, Loke J (1981b) Lung function after marathon running at warm and cold ambient temperatures. Am Rev Respir Dis 124:154–7
Mahler DA, Snyder P, Loke J (1980) Pulmonary function in runners before and after a 20-kilometer road race. Conn Med 44:549–52
McLaughlin FJ, Dozor AJ (1983) Cold air inhalation challenge in the diagnosis of asthma in children. Pediatrics 72:503–9
O'Cain DF, Dowling NB, Slutsky AS, Hensley M, Strohl K, McFadden ER, Ingram RH (1980) Airway effects of respiratory heat loss in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol 49:875–80
Stubbing DG, Pengelly LD, Morse JLC, Jones NL (1980) Pulmonary mechanics during exercise in normal males. J Appl Physiol 49:506–10
Weiner JS, Lourie JA (1969) Human biology: a guide to field methods. Blackwell, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapman, K.R., Allen, L.J. & Romet, T.T. Pulmonary function in normal subjects following exercise at cold ambient temperatures. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 60, 228–232 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00839164
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00839164