Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether supplementation with vitamin A together with iron of Indonesian pregnant women decreases morbidity and improves growth of their infants during the first year of life.
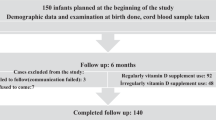
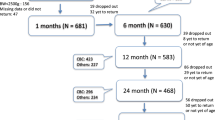
Design: Women from a rural area in West Java, Indonesia, were randomly assigned on an individual basis to double-blind supplementation once weekly from ∼18 weeks of pregnancy until delivery. Supplementation comprised 120 mg iron and 500 µg folic acid with or without 4800 RE vitamin A. Their newborn infants were followed up during the first year of life: weight, length, morbidity and food intake were assessed monthly.
Results: Infants whose mothers had taken vitamin A supplements during pregnancy had similar weight, length, weight gain and growth as their counterparts during the follow-up period. The proportions of infants with reported symptoms of morbidity were similar in the vitamin A plus iron group and the iron group. In addition immunisation coverage and feeding mode did not differ between the groups. All infants were breast-fed, but exclusive breast-feeding rapidly declined at 4 months of age. Infants with serum retinol concentrations >0.70 µmol/l increased their weight and length more during the first 6 months of life and had higher weight-for-age Z-scores during the first year of life than infants with serum retinol concentrations ≤0.70 µmol/l. Serum retinol concentrations were not associated with morbidity.
Conclusion: In this study, vitamin A supplementation in conjunction with iron supplementation of pregnant women did not improve growth or reduce morbidity of their infants during the first year of life.
Sponsorship: Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research-Netherlands Foundation for the Advancement of Tropical Research (NWO-WOTRO) (WV 93-280), the Neys-van Hoogstraten Foundation (IN 114), The Netherlands and the German Agency for Technical Cooperation (GTZ)/South East Asian Ministers of Education Organization, Tropical Medicine (SEAMEO-TROPMED), Indonesia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACC/SCN . 2000 Fourth Report on the World Nutrition Situation. Nutrition Throughout the Life Cycle. Geneva: ACC/SCN (in collaboration with IFPRI)
Adair LS, Guilkey DK . 1997 Age-specific determinants of stunting in Filipino children J. Nutr. 127: 314–320
Allen LH . 1994 Nutritional influences on linear growth: a general review Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 48: 75S–89S
Allen LH . 2000 Anemia and iron deficiency: effects on pregnancy outcome Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71: 1280S–1284S
Angeles IT, Schultink JW, Matulessi P, Gross R, Sastroamidjojo S . 1993 Decreased rate of stunting among anemic Indonesian preschool children through iron supplementation Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 58: 339–342
Beaton GH, Martorell R, Aronson KJ, Edmonston B, McCabe G, Ross AC, Harvey B . 1993 Effectiveness of vitamin A supplementation in the control of young child morbidity and mortality in developing countries. ACC/SCN State-of-the-art series, Nutrition Policy discussion paper no.13 Geneva: ACC/SCN
Christian P, West KP J, Khatry SK, Katz J, LeClerq S, Pradhan EK, Shrestha SR . 1998 Vitamin A or beta-carotene supplementation reduces but does not eliminate maternal night blindness in Nepal J. Nutr. 128: 1458–1463
Coutsoudis A, Adhikari M, Pillay K, Kuhn L, Coovadia HM . 2000 Effect of vitamin A supplementation on morbidity of low-birth-weight neonates S. Afr. Med. J. 90: 730–736
Dewey KG . 1998 Cross-cultural patterns of growth and nutritional status of breast-fed infants Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 67: 10–17
Donnen P, Brasseur D, Dramaix M, Vertongen F, Zihindula M, Muhamiriza M, Hennart P . 1998 Vitamin A supplementation but not deworming improves growth of malnourished preschool children in eastern Zaire J. Nutr. 128: 1320–1327
Frongillo EA Jr . 1999 Symposium: causes and etiology of stunting. Introduction. J. Nutr. 129: 529S–530S
Glasziou PP, Mackerras DE . 1993 Vitamin A supplementation in infectious diseases: a meta-analysis Br. Med. J. 306: 366–370
Hop LT, Gross R, Giay T, Sastroamidjojo S, Schultink W, Lang NT . 2000 Premature complementary feeding is associated with poorer growth of Vietnamese children J. Nutr. 130: 2683–2690
Humphrey JH, Rice AL . 2000 Vitamin A supplementation of young infants Lancet 356: 422–424
Kalter HD, Gray RH, Black RE, Gultiano SA . 1991 Validation of the diagnosis of childhood morbidity using maternal health interviews Int. J. Epidemiol. 20: 193–198
Katz J, West KP J, Khatry SK, Pradhan EK, LeClerq SC, Christian P, Wu LS-F, Adhikari RK, Shrestha SR, Sommer A . 2000 Maternal low-dose vitamin A or {beta}-carotene supplementation has no effect on fetal loss and early infant mortality: a randomized cluster trial in Nepal Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71: 1570–1576
Kusin JA, Kardjati S, Houtkooper JM, Renqvist UH . 1992 Energy supplementation during pregnancy and postnatal growth Lancet 340: 623–626
Kusin JA, Kardjati S, Renqvist UH, Steenbergen van WM, Koetsier D . 1994 Infant nutrition and growth In Maternal and Child Nutrition in Madura, Indonesia, ed. JA Kusin & S Kardjati 175–204 Amsterdam: Royal Tropical Institute
Labbok M, Krasovec K . 1990 Toward consistency in breastfeeding definitions Stud. Fam. Plann. 21: 226–230
LIPI . 1994 Widya Karya Pangan dan Gizi. Indonesia: LIPI
Marks GC, Habicht JP, Mueller WH . 1989 Reliability, dependability, and precision of anthropometric measurements. The Second National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1976–1980 Am. J. Epidemiol. 130: 578–587
Muhilal Permeisih D, Idjradinata YR, Muherdiyantiningsih Karyadi D . 1988 Vitamin A-fortified monosodium glutamate and health, growth, and survival of children: a controlled field trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 48: 1271–1276
Muslimatun S, Schmidt MK, Schultink W, West CE, Hautvast JGAJ, Gross R, Muhilal . 2001 Weekly supplementation with iron and vitamin A during pregnancy increases hemoglobin concentration but decreases serum ferritin concentration in Indonesian pregnant women J. Nutr. 131: 85–90
Mwanri L, Worsley A, Ryan P, Masika J . 2000 Supplemental vitamin A improves anemia and growth in anemic school children in Tanzania J. Nutr. 130: 2691–2696
Preziosi P, Prual A, Galan P, Daouda H, Boureima H, Hercberg S . 1997 Effect of iron supplementation on the iron status of pregnant women: consequences for newborns Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66: 1178–1182
Rahman MM, Mahalanabis D, Wahed MA, Islam MA, Habte D . 1995 Administration of 25,000 IU vitamin A doses at routine immunisation in young infants Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 49: 439–445
Rahman MM, Mahalanabis D, Alvarez JO, Wahed MA, Islam MA, Habte D, Khaled MA . 1996 Acute respiratory infections prevent improvement of vitamin A status in young infants supplemented with vitamin A J. Nutr. 126: 628–633
Rahmathullah L, Underwood BA, Thulasiraj RD, Milton RC . 1991 Diarrhea, respiratory infections, and growth are not affected by a weekly low-dose vitamin A supplement: a masked, controlled field trial in children in southern India Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54: 568–577
Rice AL, Stoltzfus RJ, de-Francisco A, Chakraborty J, Kjolhede CL, Wahed MA . 1999 Maternal vitamin A or beta-carotene supplementation in lactating Bangladeshi women benefits mothers and infants but does not prevent subclinical deficiency J. Nutr. 129: 356–365
Roy SK, Islam A, Molla A, Akramuzzaman SM, Jahan F, Fuchs G . 1997 Impact of a single megadose of vitamin A at delivery on breastmilk of mothers and morbidity of their infants Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 51: 302–307
Ruel MT, Rivera JA, Santizo MC, Lonnerdal B, Brown KH . 1997 Impact of zinc supplementation on morbidity from diarrhea and respiratory infections among rural Guatemalan children Pediatrics 99: 808–813
Schmidt MK, Muslimatun S, West CE, Schultink W, Hautvas JGAJ . Vitamin A and iron supplementation of Indonesian pregnant women benefits vitamin A status of their infants Br. J. Nutr. (in press)
Semba RD . 1994 Vitamin A, immunity, and infection Clin. Infect. Dis. 19: 489–499
Sommer A, West KP J . 1996 Vitamin A Deficiency. Health, Survival, and Vision. New York: Oxford University Press
Stoltzfus RJ, Hakimi M, Miller KW, Rasmussen KM, Dawiesah S, Habicht JP, Dibley MJ . 1993 High dose vitamin A supplementation of breast-feeding Indonesian mothers: effects on the vitamin A status of mother and infant J. Nutr. 123: 666–675
Tarwotjo I, Katz J, West-KP J, Tielsch JM, Sommer A . 1992 Xerophthalmia and growth in preschool Indonesian children Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55: 1142–1146
Underwood BA . 1994 Maternal vitamin A status and its importance in infancy and early childhood Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 59: 517S–522S
Victoria CG, Morris SS, Barros FC, Horta BL, Weiderpass E, Tomasi E . 1998 Breast-feeding and growth in Brazilian infants Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 67: 452–458
Waterlow JC, Schürch B . 1994 Causes and mechanisms of linear growth retardation. Proceedings of an I/D/E/C/G workshop held in London January 15–18, 1993. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 48 Suppl: S1–S216
West KP J, Katz J, Shrestha SR, LeClerq SC, Khatry SK, Pradhan EK, Adhikari R, Wu LS, Pokhrel RP, Sommer A . 1995 Mortality of infants <6 mo of age supplemented with vitamin A: a randomized, double-masked trial in Nepal Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62: 143–148
West KP, LeClerq SC, Shrestha SR, Wu LS, Pradhan EK, Khatry SK, Katz J, Adhikari R, Sommer A . 1997 Effects of vitamin A on growth of vitamin A-deficient children: field studies in Nepal J. Nutr. 127: 1957–1965
West KP J, Katz J, Khatry SK, LeClerq SC, Pradhan EK, Shrestha SR, Connor PB, Dali SM, Christian P, Pokhrel RP, Sommer A . 1999 Double blind, cluster randomised trial of low dose supplementation with vitamin A or beta carotene on mortality related to pregnancy in Nepal. The NNIPS-2 Study Group Br. Med. J. 318: 570–575
WHO/CHD Immunisation-Linked Vitamin A Supplementation Study Group . 1998 Randomised trial to assess benefits and safety of vitamin A supplementation linked to immunisation in early infancy Lancet 352: 1257–1263
WHO Working Group on Infant Growth . 1994 An Evaluation of Infant Growth. A Summary of Analyses Performed in Preparation for the WHO Expert Committee on Physical Status: the Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry in Infants. Geneva: Nutrition Unit of the WHO
World Health Organization . 1998 Safe Vitamin a Dosage During Pregnancy and Lactation Recommendations and Report of a Consultation. Geneva: WHO, Micronutrient Initiative
World Health Organization . 2000 Global Database on Child Growth and Malnutrition. Geneva: WHO
Yip R . 2000 Significance of an abnormally low or high hemoglobin concentration during pregnancy: special consideration of iron nutrition Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 72: 272S–278S
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all mothers and infants who participated in this study for their willingness to attend our monthly measurements. We thank the field workers, voluntary health workers and midwives of Leuwiliang for their contribution to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, M., Muslimatun, S., Schultink, W. et al. Randomised double-blind trial of the effect of vitamin A supplementation of Indonesian pregnant women on morbidity and growth of their infants during the first year of life. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 338–346 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601318
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601318