Abstract
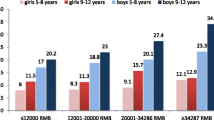
The aim of this study was to determine whether socio-economical status (SES) is associated with overweight and obesity in prepuberal children. In an area of North-Western Italy a sample of 1420 children, aged 10–11 years, had his/her height and weight recorded, (overweight and obesity were defined, respectively, as relative body weight ≥120% and ≥140%), and parents were requested to compile a questionnaire exploring some demographic and social conditions. 23% of the sample resulted overweight or obese. Prevalence rate ratios (PRR) of overweight and obesity (together) were calculated, adjusting for parents' age, parents' area of birth, and school district. PRR for mother's lowest educational level compared to the highest was 1.59 (95% CI: 1.19–2.13), while for father's education was 1.21 (0.90–1.63). PRRs for ‘unemployed’ or ‘manual’ mother compared to ‘upper non manual’ were respectively 1.83 (1.20–2.79) and 2.20 (1.31–3.68), while for ‘unemployed’ or ‘manual’ father were 2.63 (1.97–2.63), and 1.63 (1.27–2.09). The cultural resources of the mother, and the economical resources of the family seem to influence the prevalence of weight gain in prepuberal children. This should be taken into account when planning programs for the prevention or reduction of obesity in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ceratti F, Garavaglia M, Piatti L, et al. Screening dell'obesità nella popolazione scolastica della zona 20 di Milano ed intervento di educazione alimentare. Epid Prev 1990; 45: 1–8.
Maffeis C, Talamini G, Tató L. Influence of diet, physical activity and parent's obesity on children adiposity: A four-year longitudinal study. Int J Obesity 1998; 22: 758–764.
De Vito E, La Torre G, Langiano E, Berardi D, Ricciardi G. Overweight and obesity among secondary school children in Central Italy. Eur J Epidemiol 1999; 15: 649–654.
Rimm IJ, Rimm A. Association between juvenile onset of obesity and severe adult obesity in 73,532 women. Am J Public Health 1976; 66: 479–489.
Garn SM, La Velle M. Two-decade follow up of fatness in early childhood. Am J Dis Child 1985; 139: 181–185.
Sobal J, Stukard AJ. Socioeconomic status and obesity: A review of the literature. Psychol Bull 1989; 105: 260–275.
Sudquist J, Johansson SE. The influence of socioeconomic status, ethnicity and lifestyle on body mass index in a longitudinal study. Int J Epidemiol 1998; 27: 57–63.
Stukard AJ, D'Aquili E, Fox S, Filion RDL. The influence of social class on obesity and thinness in children. JAMA 1985; 221: 579–584.
Kimm SY, Obarzanek E, Barton BA, et al. Race, socioeconomic status and obesity in 9-to 10-year old girls: The NHLBI Growth and Health Study. Ann Epidemiol 1996; 6: 266–275.
Troiano RP, Flegal KM. Overweight children and adolescents: Description, epidemiology and demographics. Pediatrics 1998; 101: 497–504.
Hunter S, Frerichs PR, Webber LS, Berenson GS. Social status and cardiovascular disease risk factor variables in children: The Bogalusa Heart Study. J Chronic Dis 1979; 32: 441–449.
Khoury PR, Morrison JA, Laskarzenski P, et al. Relationships of education and occupation to coronary heart risk factors in schoolchildren and adults: The Princeton School District study. Am J Epidemiol 1981; 113: 378–395.
De Spiegalere M, Dramaix M, Hennart P. Socioeconomic status and changes in body mass from 3 to 5 years. Arch Dis Child 1998; 78: 477–478.
De Spiegalere M, Dramaix M, Hennart P. Social status and obesity during puberty. Int J Obesity 1998; 22: 268–274.
Jansen W, Hazebroek Kampschreur AA. Differences in height and weight between children living in neighbourhoods of different socioeconomic status. Acta Paediatr 1997; 86: 224–225.
Lissau-Lund-Sorensen I, Sorensen TIA. Prospective study of the influence of social factors in childhood on risk of overweight in young adulthood. Int J Obesity 1992; 16: 169–175.
Leino M, Porkka KV, Raitakari OT, Laitinen S, Taimela S, Viikari JS. Influence of parental occupation on coronary heart disease risk factors in children. The cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Int J Epidemiol 1996; 25: 1889–1895.
White E, Wilson A, Greene SA, et al. Growth screening and urban deprivation. J Med Screen 1995; 2–3: 140–144.
Duran Tauleria E, Rona RJ, Chinn S. Factors associated with weight for height and skinfold thickness in British children. J Epidemiol Community Health 1995; 49: 466–473.
Cole TJ. Weight-stature indexes to measure underweight, overweight and obesity. In: Himes JH (ed), Anthropometric Assessment of Nutritional Status, New York: Wiley-Liss, 1991; 83–111.
Himes JH, Dietz WH. Guidelines for overweight in adolescent preventive services: Recommendations from an expert committee. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 59: 307–316.
Scholler DA. Use of the body mass index (BMI) as a measure of overweight in children and adolescents. J Pediatr 1998; 132: 191–193.
Crepaldi G, Belfiore F, Bosello O, et al. Epidemiologia del sovrappeso e dell'obesità: Rapporti tra prevalenza e mortalità. In: CCI S.O.S' 91 (ed), Sovrappeso Obesità e Salute: Consensus Conference Italiana. Roma: Luigi Pozzi, 1991; 148–156.
Hamil PVV, Drizd TA, Johnson CL, Reed RB, Roche AF, Moore WM. Physical growth: National Center for Health Statistics percentiles. Am J Clin Nutr 1979; 32: 607–629.
Skov T, Deddens J, Petersen MR, Endhal L. Prevalence proportion ratios: Estimation and hypotesis testing. Int J Epidemiol 1998; 27: 91–95.
Lissner L, Heitman BL. Dietary fat and obesity: Evidence from epidemiology. Eur J Clin Nutr 1995; 49: 79–90.
Goran MI, Hunter G, Nagy TR, Johnson R. Physical activity related energy expenditure and fat mass in young children. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997; 21: 171–178.
Ravussin E, Swiburn BA. Pathophysiology of obesity. Lancet 1992; 340: 404–408.
James WP, Nelson M, Ralph A, Leather SP. Socioeconomic determinants of health. The contribution of nutrition to inequalities in health. Br Med J 1997; 314: 1545–1549.
Guillaume M, Lapidus L, Lambert A. Obesity and nutrition in children. The Belgian Luxembourg Child Study IV. Eur J Clin Nutr 1998; 52: 323–328.
Guillaume M, Lapidus L, Bjorntorp P, Lambert A. Physical activity, obesity and cardiovascular risk factors in children. The Belgian Luxembourg Child Study II. Obes Res 1997; 5: 549–556.
Vannoni F, Burgio A, Quattrociocchi L, Costa G, Faggiano F. Differenze sociali e indicatori di salute soggettiva, malattie croniche, disabilità e stili di vita nell'indagine ISTAT sulla salute del 1994. Epid Prev 1999; 23: 207–214.
Bostrom G, Diderichsen F. Socioeconomic differentials in misclassification of height, weight and body mass index based on questionnaire data. Int J Epidemiol 1997; 26: 860–866.
Liberatos P, Lik BG, Kesley JL. The measurements of social class in epidemiology. Epidemiol Rev 1988; 10: 87–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnavi, R., Spagnoli, T., Galotto, C. et al. Socioeconomic status, overweight and obesity in prepuberal children: A study in an area of Northern Italy. Eur J Epidemiol 16, 797–803 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007645703292
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007645703292