Abstract
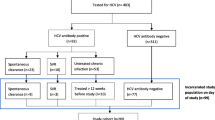
Objective: Determine the incidence of hepatitis C virus antibodies among a cohort of prisoners. Design: Follow-up study of a random sample of prisoners who participated in a cross-sectional survey in 1996. Setting: 29 correctional centres in New South Wales (Australia). Participants: 181 adult prisoners (163 men and 18 women). Results: The incidence of hepatitis C virus antibody among the 90 inmates who were seronegative at the first test in 1996 was 7.1 per 100 person-years (16 seroconverters). Among the 90 inmates, 37 had re-entered the prison system following release into the community and 53 had been continuously detained. The seroconversion rate was higher among the re-entrants compared with those who had been continuously incarcerated (10.8 vs. 4.5 per 100 person-years, p=0.07). However, when the data was stratified by injecting status, the seroconversion rate in the two groups was similar. Most of the seroconverters had histories of injecting drug users (14/16). The overall incidence among injectors was 19.3 per 100 person years (95% CI: 9.1–29.2). Conclusions: Hepatitis C transmission occurs inside the prison with injecting drug use the likely cause. Among non-injectors, tattooing was the most likely mode of transmission. Harm minimisation measures with proven effectiveness need to be considered for this environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N Crofts T Stewart P Hearne (1996) ArticleTitleSpread of blood borne viruses among Australian prison entrants Br Med J 310 285–288
D Vlahov KE Nelson TC Quinn N Kendig (1993) ArticleTitlePrevalence and incidence of hepatitis C virus infection among male prison inmates in Maryland Eur J Epidemiol 9 566–569 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00209538 Occurrence Handle8307145 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC3sbovVc%3D
PB Christensen HB Krarup HG Niesters H Norder J Georgsen (2000) ArticleTitlePrevalence and incidence of bloodborne viral infections among Danish prisoners Eur J Epidemiol 16 1043–1049 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1010833917242 Occurrence Handle11421474 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzmtVyrsA%3D%3D
M Malliori V Sypsa M Psichogiou et al. (1998) ArticleTitleA survey of bloodborne viruses and associated risk behaviours in Greek prisons Addiction 92 243–251
TG Butler KA Dolan MJ Ferson LM McGuinness PR Brown PW Robertson (1997) ArticleTitleHepatitis B and C in New South Wales prisons: Prevalence and risk factors Med J Aust 166 127–130 Occurrence Handle9059433 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB3M3lvFQ%3D
T Butler J Spencer J Cui K Vickery J Zou J Kaldor (1999) ArticleTitleSeroprevalence of markers for hepatitis B, C and G in male and female prisoners–NSW, 1996 Aust NZ J␣Pub Health 23 384
I van Beek R Dwyer GJ Dore K Luo J Kaldor (1998) ArticleTitleInfection with HIV and hepatitis C virus among injecting drug users in a prevention setting: Retrospective cohort study Br Med J 317 433–437 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czmvV2itQ%3D%3D
BP Smyth JJ O’Connor J Barry E Keenan (2003) ArticleTitleRetrospective cohort study examining incidence of HIV and hepatitis C infection among injecting drug users in Dublin J Epidemiol Commun Health 57 310–311 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s7jt1ersA%3D%3D
DM Patrick MW Tyndall GA Cornelisse et al. (2001) ArticleTitleIncidence of hepatitis C virus infection among injection drug users during an outbreak of HIV infection Can Med Ass J 165 889–895 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mrlt1KitA%3D%3D
D Indermauer K Upton (1998) ArticleTitleAlcohol and drug use patterns of prisoners in Perth Aust NZJ Criminol 3 144–167
Butler T. Preliminary findings of the NSW Inmate Health Survey. 1997. NSW Corrections Health Service. ISBN 07313 40981.
Butler T, Milner L. The 2001 Inmate Health Survey. 2003. Sydney, Corrections Health Service. ISBN: 0 7347 3560 X.
S Gore G Bird A Ross (1995) ArticleTitlePrison rites: Starting to inject inside Br Med J 311 1135–1136 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymD2cfosFA%3D
T Butler M Levy K Dolan J Kaldor (2003) ArticleTitleDrug use and its correlates in an Australian prisoner population Addict Res Theor 11 89–101
A Arrada O Kak Dit Zbar V Vesseur (2001) ArticleTitlePrevalence of HBV and HCV infections and incidence of HCV infection after 3, 6 and 12 months detention in La Sante prison, Paris Ann Med Interne 152 IssueIDSuppl 6–8
J Post K Dolan R Whybin I Carter P Haber A Lloyd (2001) ArticleTitleAcute hepatitis C virus infection in an Australian prison inmate: tattooing as a possible transmission route Med J Aust 174 183–184 Occurrence Handle11270759 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7nsFyitg%3D%3D
P Haber S Parsons S Harper P White W Rawlinson A Lloyd (1999) ArticleTitleTransmission of hepatitis C within Australian prisons Med J Aust 171 31–33 Occurrence Handle10451669 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzotV2ktA%3D%3D
S Darke (1998) ArticleTitleSelf-report among injecting drug users: A review Drug Alcohol Dependence 51 253–263 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FgsValtA%3D%3D
Return on Investment in Needle and Syringe Programs in Australia. 2002. Canberra, Commonwealth Department of Health and Ageing. ISBN 0 642 82116 X.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butler, T., Kariminia, A., Levy, M. et al. Prisoners are at risk for hepatitis C transmission. Eur J Epidemiol 19, 1119–1122 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-004-1705-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-004-1705-9